Have you ever noticed how some men seem to radiate heat more than others? This intriguing phenomenon can be quite perplexing, particularly when it leads to discomfort in social situations or affects personal relationships. Understanding why men radiate heat is essential not only for social harmony but also for grasping the biological and hormonal underpinnings that contribute to this experience. This exploration will unveil the hidden mechanisms behind men’s heat generation and how hormones play a critical role in temperature regulation.
The Biological Mechanisms Behind Men’s Heat Generation
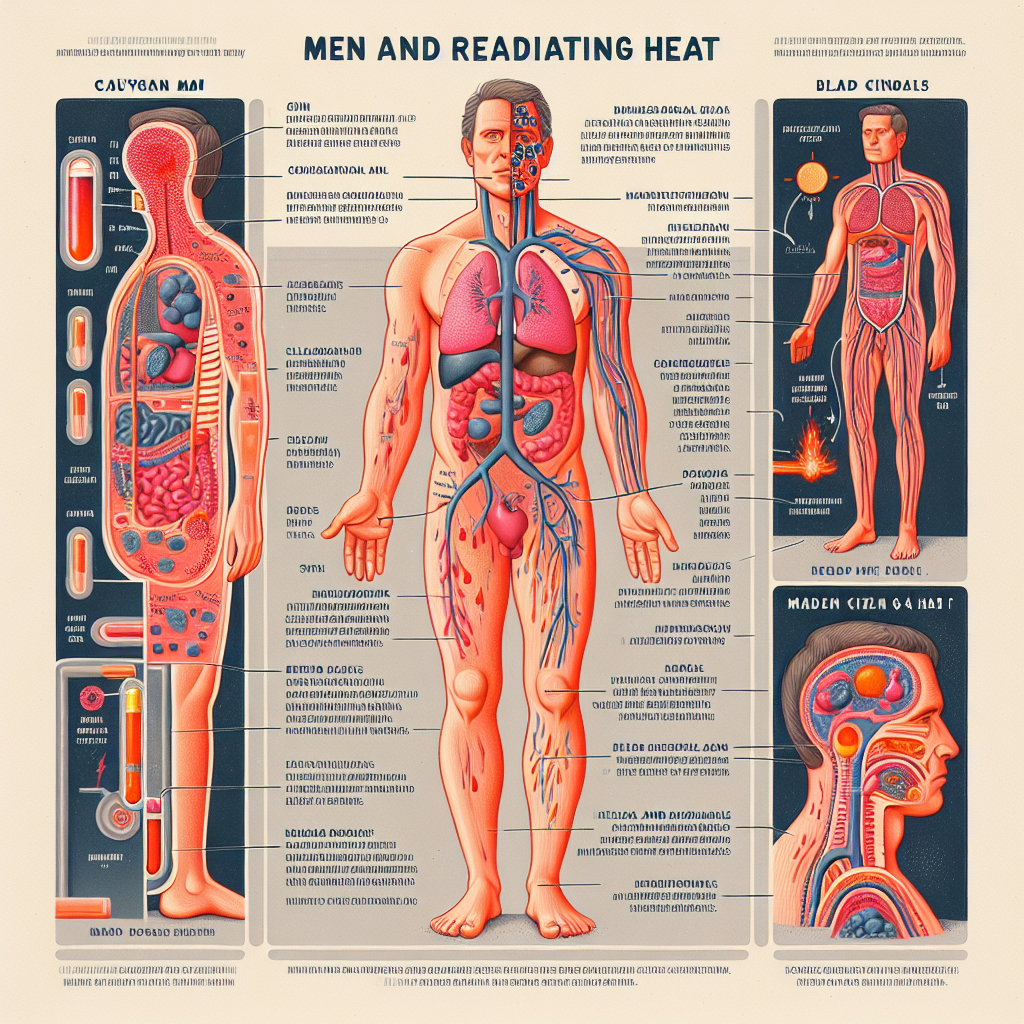
Men typically have a higher basal metabolic rate compared to women, which significantly contributes to their heat generation. This difference arises from the larger muscle mass that men generally possess, as muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue. Consequently, this elevated caloric expenditure leads to an increase in body heat. Muscle cells are metabolically active and produce heat as a byproduct of energy consumption. Thus, men are often found to have a warmer body temperature, especially during physical exertion or in social settings where they may be more active.
Moreover, the thermoregulation process in men is influenced by the body’s physiological response to environmental changes. The hypothalamus, a small region in the brain, plays a critical role in regulating body temperature. When the body’s temperature rises, the hypothalamus signals the sweat glands to produce sweat, which cools the body as it evaporates. While this mechanism is common to all humans, men often sweat more profusely due to the larger number of sweat glands and the efficiency of their thermoregulation, further contributing to their perceived heat radiance.
Additionally, another key factor lies in the circulatory system. Men typically have a larger heart and greater blood volume, resulting in increased blood circulation throughout the body. This enhanced blood flow can lead to higher skin temperatures, which may be particularly noticeable in social situations where emotions run high. As blood vessels dilate to release heat, men can appear warmer in both physical and emotional contexts, making this a noteworthy aspect of their biological makeup.
The Impact of Hormones on Temperature Regulation in Men
Hormones are integral to understanding the thermal differences between genders, particularly testosterone. This male hormone not only contributes to muscle growth and strength but also influences metabolism. Elevated testosterone levels can lead to a more robust metabolic process, causing men to generate and retain more heat compared to women. This hormonal effect means that fluctuations in testosterone can significantly impact how warm a man feels, particularly during periods of physical activity or emotional stress.
Another critical hormone involved in temperature regulation is cortisol, a steroid hormone associated with stress. When men experience stress, cortisol levels rise, which can lead to an increase in metabolic rate and, subsequently, heat production. This relationship suggests that the emotional and psychological states of men can directly influence their thermal output, causing them to radiate more heat in high-pressure situations or during times of anxiety. Understanding this connection can equip men and those around them with strategies to manage heat generation during stressful moments.
Estrogen, while primarily a female hormone, also plays a role in men’s temperature regulation. Although men have lower levels of estrogen, it still influences body fat distribution and metabolic rates. The interplay between testosterone and estrogen can create a dynamic balance in how heat is produced and dissipated in male bodies. When estrogen levels fluctuate, especially during certain life stages or health conditions, men may experience changes in their heat radiance, adding another layer to the complexity of male thermoregulation.
Understanding why men radiate heat delves into a fascinating interplay of biological mechanisms and hormonal influences. By grasping these elements, both men and their social circles can better navigate temperature-related social discomforts. If you find yourself affected by this phenomenon, consider exploring ways to manage personal heat generation or appreciate the underlying biology that contributes to this experience. Engaging in conversations about health and well-being can also promote greater awareness and comfort among those who experience these thermal differences. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, stress management techniques, or simply educating fellow peers, the insights gained from this exploration can enhance both personal and social interactions.
Managing Degenerative Disc Disease: The Role of YogaSubmitting Your Web Wrapped Curio: A Step-by-Step GuideStrategic Hiding Spots in Life is Strange Pool SceneRelevant LinkRelevant LinkRelevant LinkExploring the Impact of 40,000 Daily Steps on Weight LossEffective Yoga Poses for Optimal Weight Loss and WellnessComprehensive Reviews of Happy Mammoth Weight Loss ProgramRelevant LinkRelevant LinkRelevant Link